Market Access and Exports

Do you want to develop your business? Learning about market access and exporting will help you grow sustainably and enhance your competitive edge.
Market Research
![]() Should your business provide a new product or service to existing customers or aim to enter a new market and find new customers? Market research will help you find the answers and make good decisions.
Should your business provide a new product or service to existing customers or aim to enter a new market and find new customers? Market research will help you find the answers and make good decisions.

Market Research Questions
First you should complete a business plan. Once you have developed your idea you can identify your customer base by obtaining the following information:
- Which type of clients will want your products or services?
- How much are they willing to spend?
- Through which media outlets will they learn about your business?
- Where would they want to buy your products or services?
Identify Sales Channels in the New Market
The Financial Times defines “sales channel” as a way in which a company supplies its products or services to customers. Keep in mind that even when you are successful with one sales channel in one market, that sales channel may fail when you expand into a new market. When expanding into a new market, you may have to try new sales channels as well. It may also take time to build relationships with distributors in the new market, so patience and persistence are essential. Once your product has reached a level of proven success, you will be able to access new channels such as third-party distributors, value-added resellers, or large product expos and conferences.
Expanding into an international market for the first time is a challenge. You will need to learn about tariffs and international trade laws, cultural differences, and differences in consumer preferences. It will be more difficult for you to do direct research, so online information resources related to your target market are essential.
Negotiating Contracts with International Partners

Signing contracts with international partners
When negotiating with an international partner, make sure contract language is airtight, particularly in the rights and obligations of the parties. Make sure the dispute settlement process is transparent and does not create a biased settlement process or legal trap for your business. Make sure that information or provisions to ensure payment are clear and specific. The contract should specify the payment amounts and timelines, whether any delay in payment is allowable, and whether interest or fees will apply on delayed payments.
Hiring a lawyer who specializes in international contracts is always a good idea. It may be a considerable expense for a new company, but the lawyer’s expertise can prevent you from making mistakes that will cost far more money in the future. This is especially important if your international partner is a large corporation, as they have large legal teams for this purpose.
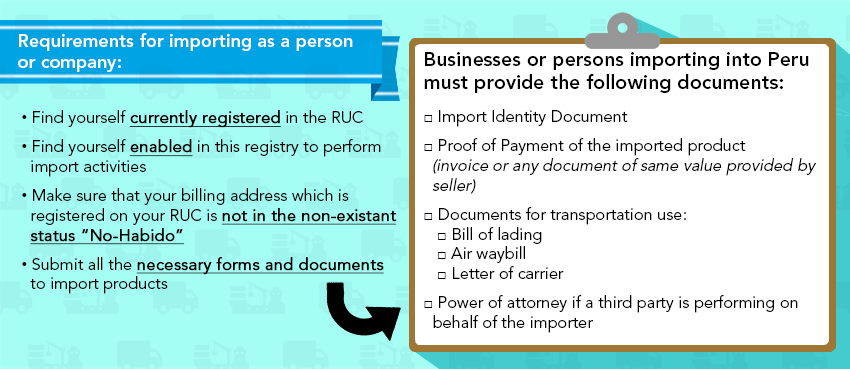
Peru Customs Procedures
![]()
Importing modalities in Peru
- For imports under $200.00 US, there is no need to undergo any procedures or pay import fees
- For imports of between $200.00 US and $2000.00 US, import taxes can be cancelled at any financial entity
- Simplified Import Dispatch: Non-commercial value samples, gifts under $ 1,000 US or products under $ 2,000 US can be imported directly and without a customs broker. You will need to make a Simplified Import Declaration (DSI). You can use IMPORTA FACIL, a system that allows you to import merchandise through the national postal service.
- Definitive Import: For imports valued above $ 2,000.00 US, fill out a Customs Declaration of Merchandise (DAM) with the help of a customs broker.
Exporting from Peru
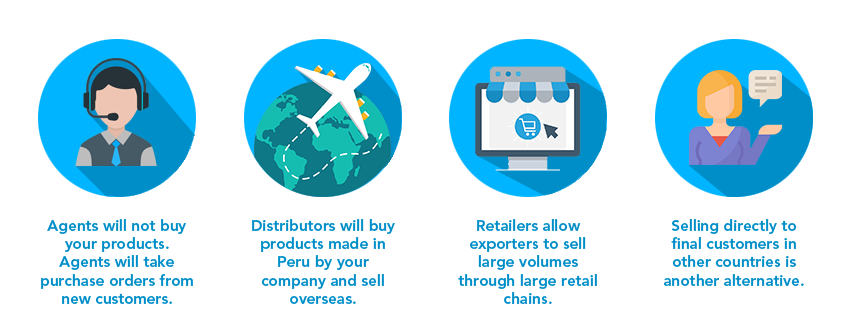
Your business can export directly and indirectly. With indirect exports, a third party manages some or all the activities related to the export and assumes full responsibility. When exporting directly, your company deals openly with the international client.
If this is the first time your business exports, it might be a good idea to take the least possible risk by exporting indirectly. Once you gain experience, begin transitioning to direct exporting. You can access international markets through the sale to national customers who will then export your product or service. This export process is straightforward and the other party will decide where and how to export. When MSMEs are not ready to export directly, businesses that choose a third party to enter new markets export indirectly. This is an efficient way to access international markets without having to manage the export. However, it is essential to find a good intermediary that has established customers for your products. An alternative is to create an export company with other MSMEs.
Direct exporting allows you to control the whole export process and the quality of customer service. This includes more profits and the possibility to build a direct relationship with new customers.
It is vital to consider sales channels that include agents, distributors, retailers and final customers.
Required Documents for Exporting Guide
To facilitate the filling of documents used in the export process, the Export Facilitation Department from the Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism offers a practical guide to help MSMEs fill export documents correctly, complying with regulations for a successful procedure. http://www.sunat.gob.pe/orientacAduana/index.html
Tariffs and Taxes
Import tariff and taxes: For a synthesis of the taxes and tariffs imposed on the importation of goods, follow this link.
Export tariff and taxes: Exports are exempt from payment of taxes. Payments are only required to services related to shipping of merchandise to be exported.
Trade Agreements
Signed free trade agreements (in force):
- World Trade Organization and Multilateral Trade Accords contained in the Final Act of the Uruguay Round Agreement
- Cartagena Accord – Andean Sub-regional Integration Agreement - Andean Community (CAN) – Member countries: Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru; Associate countries: Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Paraguay and Uruguay; Observer country: Spain
- Pacific Alliance (Chile, Colombia, Mexico, Peru)
- Peru – European Free Trade Association (EFTA)
- Peru – Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)
- Peru - Chile Free Trade Agreement (Acuerdo de Complementación Económica (ACE N° 38)
- Peru - China Free Trade Agreement
- Peru - European Union Trade Agreement
- Peru - Japan Agreement for an Economic Partnership
- Peru - MERCOSUR Economic Complementation Trade Agreement
- Peru - Cuba Economic Complementation Agreement No 50 (ACE 50)
- Peru - Mexico Trade Integration Agreement
- Peru - Singapore Free Trade Agreement
- Peru - South Korea Free Trade Agreement
- Peru - United States Trade Promotion Agreement
- Peru - Honduras Free Trade Agreement
- Peru - Costa Rica Free Trade Agreement
- Peru - Panama Free Trade Agreement
- Peru - Canada Free Trade Agreement
- Peru – Venezuela Partial Scope Agreement of Commercial Nature
Unratified trade agreements:
- Trans Pacific Partnership (TPP)
- Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP TPP11 TPP 11)
- Peru - Guatemala Free Trade Agreement
- Peru – Brazil Economic Trade Deepening Agreement
- Peru – Australia Free Trade Agreement
Ongoing negotiation trade agreements:
- Peru – World Trade Organization DOHA Program for Development
- Peru – World Trade Organization Trade in Services Agreement (TISA)
- Peru – El Salvador Free Trade Agreement
- Peru – India Free Trade Agreement
- Peru – Turkey Free Trade Agreement
Learning More
Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism (MINCETUR)
If you have any questions or need advice, you can email the Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism by clicking here, or speak to a real person by dialing 513-6120 for consultations about trade agreements.
Commercial and Credit Guide for the User of Foreign Trade (PEPE MSME SERIES)
Download from this link an instruction guide for MSMEs and entrepreneurs seeking to import and export.
Importer’s Guide (In Spanish)
This is the ABC guide to foreign trade for the importer. This guide provides general information about importing foreign goods which will be consumed or transformed into third products for sale in Peru or exported internationally.
This is the ABC guide to foreign trade for the exporter. This guide provides information about procedures and processes required to export your products to another country.
This Ministry of Foreign Trade and Tourism website provides links to other sources of information designed to help you save time and money.
What you need to know about free trade agreements
To request preferential tariff treatment or access preferential regimes in which Peru is a beneficiary, importers need to have a Certificate of Origin (Declaration of Origin) that complies with the specific trade agreement or preferential regime in the destination country.
Remember that to obtain your proof of origin; your trade operator should use one of the three alternatives designated in the trade agreement or preferential regime:
1. Self-Certification
- When the certificate of origin is issued by the commercial operator
2. Certification by Entities
- Proof of origin must be provided by an entity designated by MINCETUR
- Guide for Certificate of Origin emission
- A sworn declaration of merchandise origin
- Instructions on how to obtain a Sworn Declaration of Merchandise Origin
3. Authorized Exporter
- If the exporter of products is designated as “Authorized Exporter” he or she will be able to provide origin declarations for exported merchandise
Market Access Map, developed by the International Trade Centre, is an online interactive tool based on a worldwide database of tariff rates, export-import statistics, tariff rate quotas, and market conditions. Using this tool, you can explore information on customs tariffs, trade barriers, and rules of origin you must comply with to qualify for a preferential tariff rate.
Trade Map, developed by the International Trade Centre, is a free online tool to help enterprises learn about strategic markets. Trade Map provides yearly trade data for 220 countries and territories and all 5,300 products of the Harmonized System defined at the two-, four-, or six-digit level. Users can search for international demand, alternative markets, and competitors. Trade Map provides information in the form of tables, graphs, and maps, and allows users to filter data by goods, country, product category, or national category.
Important Laws
Learn about operating regulations and resources available for your MSME will help promote its products and services, develop business and improve productivity:
Operating regulations for the MSMEs Fund – SEPYMEX is the Small and Medium Enterprise Support Fund that promotes access to financing for MSMEs through a coverage program CREDITS FOR EXPORT (before and after shipment) facilitated by financial institutions to promote international trade. (DECRETO DE URGENCIA No 050-2002)
Learn about the Legislative Decree That Approves the Law of Promotion of Competitiveness, Formalization, and Development of the Micro and Small Enterprise and Access to Decent Employment (DECRETO LEGISLATIVO No 1086)
Unique Order Text of the Law of Promotion of Productive Development and Business Growth (DECRETO SUPREMO No 013-2013-PRODUCE)
Law That Establishes Dispositions for the Support of Productive Competitiveness (LEY No 29337)
Law That Establishes Measures to Promote Economic Growth (LEY No 30264)
Bill of Constitutional Reform that Recognizes Explicitly the Promotion of Micro and Small Businesses (MSMEs) (PROYECTO DE LEY No 187/2017-CR)
Ley que fomenta la exportación de servicios y el turismo LEY Nº 30641
Sierra y Selva Exportadora aims to boost the economic activity of the rural areas of the mountains and jungle, in order to achieve the access of small and medium producers to markets in a sustainable and competitive way, contributing to poverty reduction.